orx-noise
A collection of noise generator functions. Source and extra documentation can be found in the orx-noise sourcetree.
Prerequisites
Assuming you are working on an openrndr-template based project, all you have to do is enable orx-noise in the orxFeatures set in build.gradle.kts and reimport the gradle project.
Uniformly distributed random values
The library provides extension methods for Double, Vector2, Vector3, Vector4 to create random vectors easily. To create scalars and vectors with uniformly distributed noise you use the uniform extension function.
val d1 = Double.uniform(0.0, 640.0)
val v2 = Vector2.uniform(0.0, 640.0)
val v3 = Vector3.uniform(0.0, 640.0)
val v4 = Vector4.uniform(0.0, 640.0)
To create multiple samples of noise one uses the uniforms function.
val v2 = Vector2.uniforms(100, Vector2(0.0, 0.0), Vector2(640.0, 640.0))
val v3 = Vector3.uniforms(100, Vector3(0.0, 0.0, 0.0), Vector3(640.0, 640.0, 640.0))
The Random class can also be used to generate Double numbers and vector, but also booleans and integers.
// Boolean
val b = Random.bool(probability = 0.2)
// Int
val i1 = Random.int(0, 640)
val i2 = Random.int0(640)
// Double
val d2 = Random.double(0.0, 640.0)
val d3 = Random.double0(640.0)
// Vectors
val v2 = Random.vector2(0.0, 640.0)
val v3 = Random.vector3(0.0, 640.0)
val v4 = Random.vector4(0.0, 640.0)
Perlin, Value and Simplex noise
Random.perlin() and Random.value() accept 2D and 3D arguments. Random.simplex() up to 4D. They all return a Double. Some examples:
// Test vectors to use
val v2 = Vector2(0.1, 0.2)
val v4 = Vector4(0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4)
// Now generate random values
val d1 = Random.perlin(0.1, 0.2)
val d2 = Random.perlin(v2)
val d3 = Random.value(0.1, 0.2, 0.3)
val d4 = Random.simplex(v4)
Uniform ring noise
val v2 = Vector2.uniformRing(0.0, 300.0)
val v3 = Vector3.uniformRing(0.0, 300.0)
val v4 = Vector4.uniformRing(0.0, 300.0)
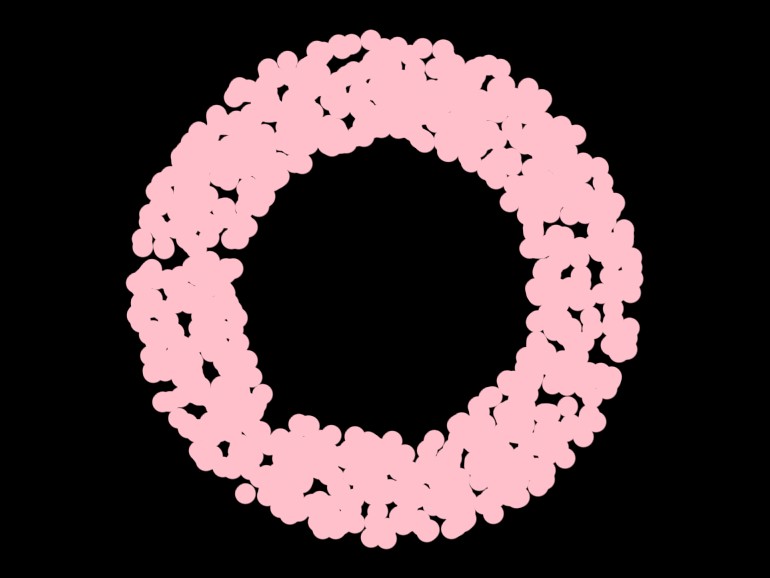
fun main() = application {
program {
extend {
drawer.fill = ColorRGBa.PINK
drawer.stroke = null
drawer.translate(width / 2.0, height / 2.00)
for (i in 0 until 1000) {
drawer.circle(Vector2.uniformRing(150.0, 250.0), 10.0)
}
}
}
}
Perlin noise
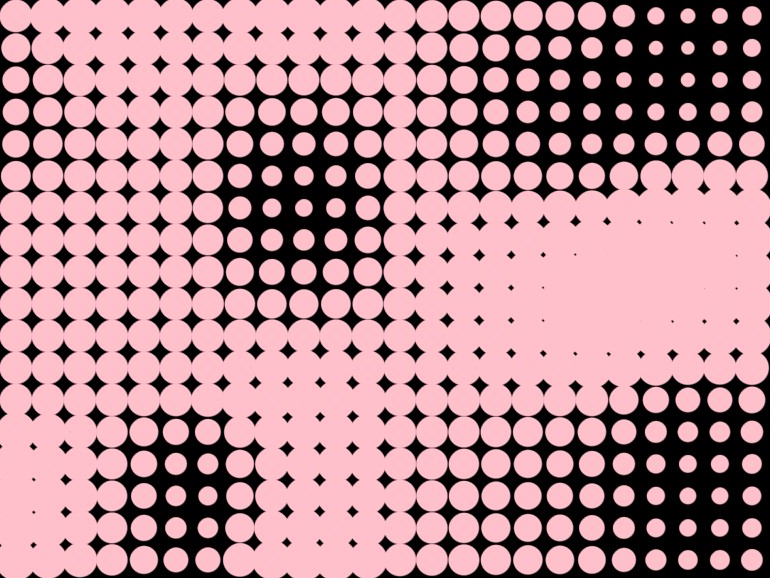
fun main() = application {
program {
extend {
drawer.fill = ColorRGBa.PINK
drawer.stroke = null
val scale = 0.005
for (y in 16 until height step 32) {
for (x in 16 until width step 32) {
val radius = perlinLinear(100, x * scale, y * scale) * 16.0 + 16.0
drawer.circle(x * 1.0, y * 1.0, radius)
}
}
}
}
}
Value noise
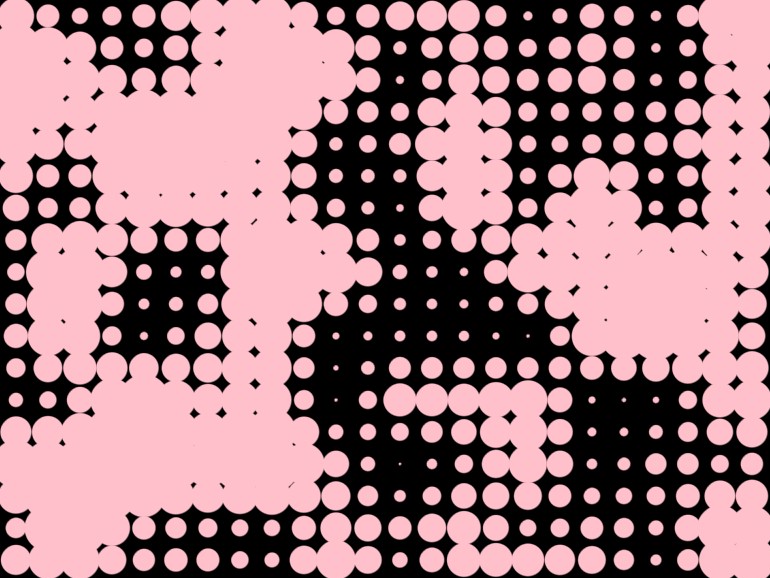
fun main() = application {
program {
extend {
drawer.fill = ColorRGBa.PINK
drawer.stroke = null
val scale = 0.0150
for (y in 16 until height step 32) {
for (x in 16 until width step 32) {
val radius = valueLinear(100, x * scale, y * scale) * 16.0 + 16.0
drawer.circle(x * 1.0, y * 1.0, radius)
}
}
}
}
}
Simplex noise
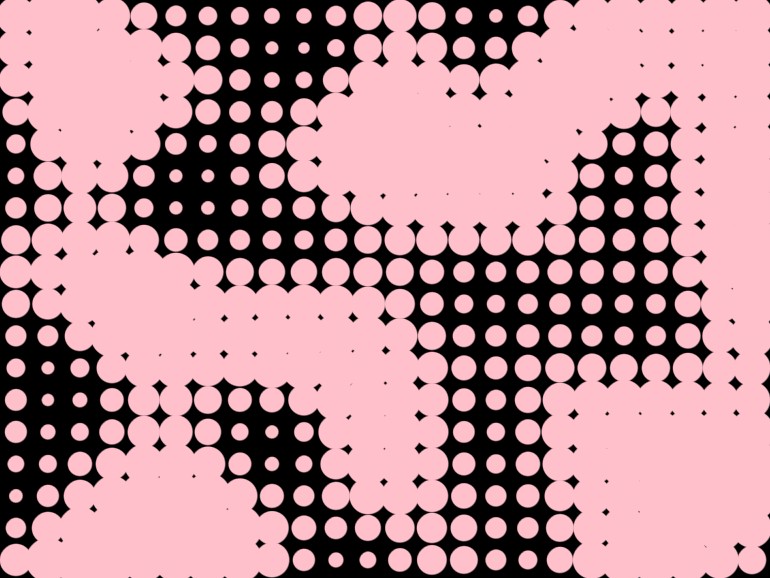
fun main() = application {
program {
extend {
drawer.fill = ColorRGBa.PINK
drawer.stroke = null
val scale = 0.004
for (y in 16 until height step 32) {
for (x in 16 until width step 32) {
val radius = simplex(100, x * scale, y * scale) * 16.0 + 16.0
drawer.circle(x * 1.0, y * 1.0, radius)
}
}
}
}
}
Fractal/FBM noise
fun main() = application {
program {
extend {
drawer.fill = ColorRGBa.PINK
drawer.stroke = null
val s = 0.0080
val t = seconds
for (y in 4 until height step 8) {
for (x in 4 until width step 8) {
val radius = when {
t < 3.0 -> abs(fbm(100, x * s, y * s, t, ::perlinLinear)) * 16.0
t < 6.0 -> billow(100, x * s, y * s, t, ::perlinLinear) * 2.0
else -> rigid(100, x * s, y * s, t, ::perlinLinear) * 16.0
}
drawer.circle(x * 1.0, y * 1.0, radius)
}
}
}
}
}
Noise gradients
Noise functions have evaluable gradients, a direction to where the value of the function increases the fastest. The gradient1D, gradient2D, gradient3D and gradient4D functions can be used to estimate gradients for noise functions.
fun main() = application {
program {
extend {
drawer.fill = null
drawer.stroke = ColorRGBa.PINK
drawer.lineCap = LineCap.ROUND
drawer.strokeWeight = 3.0
val t = seconds
for (y in 4 until height step 8) {
for (x in 4 until width step 8) {
val g = gradient3D(::perlinQuintic, 100, x * 0.005, y * 0.005, t, 0.0005).xy
drawer.lineSegment(Vector2(x * 1.0, y * 1.0) - g * 2.0, Vector2(x * 1.0, y * 1.0) + g * 2.0)
}
}
}
}
}
Gradients can also be calculated for the fbm, rigid and billow versions of the noise functions. However, we first have to create a function that can be used by the gradient estimator. For this .fbm(), .billow(), and .rigid() can be used (which works through partial application).
fun main() = application {
program {
val noise = simplex3D.fbm(octaves = 3)
extend {
drawer.fill = null
drawer.stroke = ColorRGBa.PINK
drawer.lineCap = LineCap.ROUND
drawer.strokeWeight = 1.5
val t = seconds
for (y in 4 until height step 8) {
for (x in 4 until width step 8) {
val g = gradient3D(noise, 100, x * 0.002, y * 0.002, t, 0.002).xy
drawer.lineSegment(Vector2(x * 1.0, y * 1.0) - g * 1.0, Vector2(x * 1.0, y * 1.0) + g * 1.0)
}
}
}
}
}
Noise filters
The library contains a number of Filters with which noise image can be generated efficiently on the GPU.
Hash noise
A white-noise-like noise generator.
| Parameter | Default value | Description |
|---|---|---|
seed | 0.0 | Noise seed |
gain | Vector4(1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.0) | Noise gain per channel |
bias | Vector4(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0) | Value to add to the generated noise |
monochrome | true | Outputs monochrome noise if true |
premultipliedAlpha | true | Outputs premultiplied alpha if true |

fun main() = application {
program {
val cb = colorBuffer(width, height)
val hn = HashNoise()
extend {
hn.seed = seconds
hn.apply(emptyArray(), cb)
drawer.image(cb)
}
}
}
3D Simplex noise filter
The SimplexNoise3D filter is based on Ken Perlin’s improvement over Perlin noise, but with fewer directional artifacts and, in higher dimensions, a lower computational overhead.
| Parameter | Default value | Description |
|---|---|---|
seed | Vector3(0.0, 0.0, 0.0) | Noise seed / offset |
scale | Vector3(1.0, 1.0, 1.0) | The noise scale at the first octave |
octaves | 4 | The number of octaves |
gain | Vector4(0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5) | Noise gain per channel per octave |
decay | Vector4(0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5) | Noise decay per channel per octave |
bias | Vector4(0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5) | Value to add to the generated noise |
lacunarity | Vector4(2.0, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0) | Multiplication of noise scale per octave |
premultipliedAlpha | true | Outputs premultiplied alpha if true |
fun main() = application {
program {
val cb = colorBuffer(width, height)
val sn = SimplexNoise3D()
extend {
sn.seed = Vector3(0.0, 0.0, seconds * 0.1)
sn.scale = Vector3.ONE * 2.0
sn.octaves = 8
sn.premultipliedAlpha = false
sn.apply(emptyArray(), cb)
drawer.image(cb)
}
}
}
Cell noise
A cell, Worley or Voronoi noise generator
| Parameter | Default value | Description |
|---|---|---|
seed | Vector2(0.0, 0.0) | Noise seed / offset |
scale | Vector2(1.0, 1.0) | The noise scale at the first octave |
octaves | 4 | The number of octaves |
gain | Vector4(1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.0) | Noise gain per channel per octave |
decay | Vector4(0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5) | Noise decay per channel per octave |
bias | Vector4(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0) | Value to add to the generated noise |
lacunarity | Vector4(2.0, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0) | Multiplication of noise scale per octave |
premultipliedAlpha | true | Outputs premultiplied alpha if true |
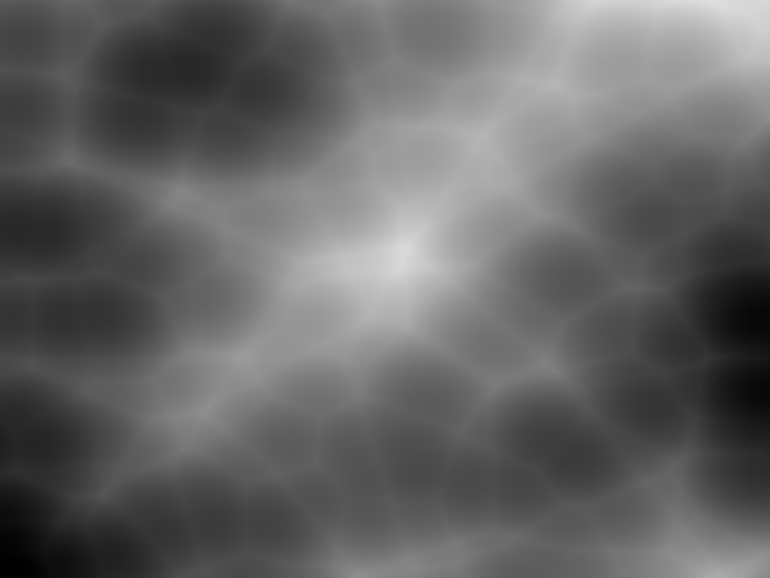

fun main() = application {
program {
val cb = colorBuffer(width, height)
val cn = CellNoise()
extend {
cn.octaves = 4
cn.apply(emptyArray(), cb)
drawer.image(cb)
}
}
}
Speckle noise
A speckle noise generator.
| Parameter | Default value | Description |
|---|---|---|
color | ColorRGBa.WHITE | Speckle color |
density | 1.0 | Speckle density |
seed | 0.0 | Noise seed |
noise | 0.0 | Speckle noisiness |
premultipliedAlpha | true | Outputs premultiplied alpha if true |

fun main() = application {
program {
val cb = colorBuffer(width, height)
val sn = SpeckleNoise()
extend {
sn.seed = seconds
sn.apply(emptyArray(), cb)
drawer.image(cb)
}
}
}
Value noise
The ValueNoise filter generates a simple fractal noise. Value noise is a computationally cheap form of creating ‘smooth noise’ by interpolating random values on a lattice.
| Parameter | Default value | Description |
|---|---|---|
seed | Vector2(0.0, 0.0) | Noise seed / offset |
scale | Vector2(1.0, 1.0) | The noise scale at the first octave |
octaves | 4 | The number of octaves |
gain | Vector4(1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.0) | Noise gain per channel per octave |
decay | Vector4(0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5) | Noise decay per channel per octave |
bias | Vector4(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0) | Value to add to the generated noise |
lacunarity | Vector4(2.0, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0) | Multiplication of noise scale per octave |
premultipliedAlpha | true | Outputs premultiplied alpha if true |
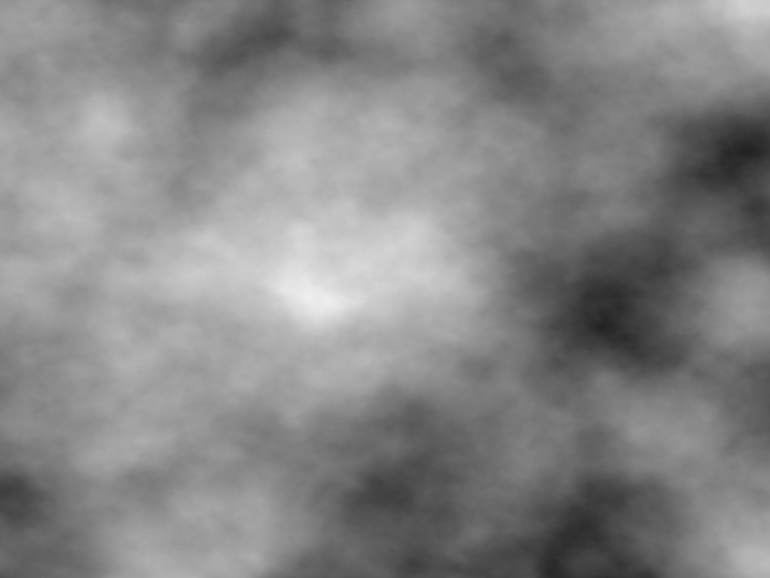

fun main() = application {
program {
val cb = colorBuffer(width, height)
val vn = ValueNoise()
extend {
vn.scale = Vector2.ONE * 4.0
vn.gain = Vector4.ONE * 0.5
vn.octaves = 8
vn.apply(emptyArray(), cb)
drawer.image(cb)
}
}
}