Images
Images are stored in ColorBuffer instances, the image data resides in GPU memory
Loading and drawing images
Images are loaded using the loadImage function and drawn using Drawer.image.
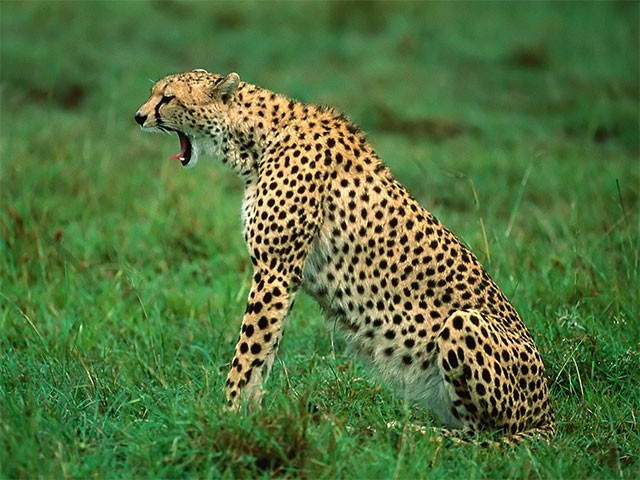

fun main() = application {
configure {}
program {
val image = loadImage("data/images/cheeta.jpg")
extend {
drawer.image(image)
}
}
}
To change the location of the image one can use Drawer.image with extra coordinates provided.
drawer.image(image, 40.0, 40.0)
Extra width and height arguments can be provided to draw a scaled version of the image.
drawer.image(image, 40.0, 40.0, 64.0, 48.0)
To rotate an image (or any other element you draw) apply transformations.
Drawing parts of images
It is possible to draw parts of images by specifying source and target rectangles. The source rectangle describes the area that should be taken from the image and presented in the target rectangle.

fun main() = application {
program {
val image = loadImage("data/images/cheeta.jpg")
extend {
val source = Rectangle(0.0, 0.0, 320.0, 240.0)
val target = Rectangle(160.0, 120.0, 320.0, 240.0)
drawer.image(image, source, target)
}
}
}
Drawing many parts of images
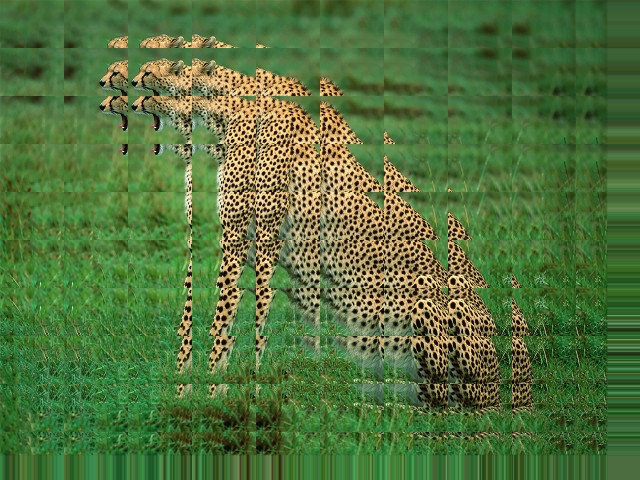
fun main() = application {
program {
val image = loadImage("data/images/cheeta.jpg")
extend {
val areas = (0..10).flatMap { y ->
(0..10).map { x ->
val source = Rectangle(x * (width / 10.0), y * (height / 10.0), width / 5.0, height / 5.0)
val target = Rectangle(x * (width / 10.0), y * (height / 10.0), width / 10.0, height / 10.0)
source to target
}
}
drawer.image(image, areas)
}
}
}
Changing the appearance of images
A linear color transform can be applied to images by setting Drawer.drawStyle.colorMatrix to a Matrix55 value.
Tinting
Tinting multiplies the image color with a tint color.
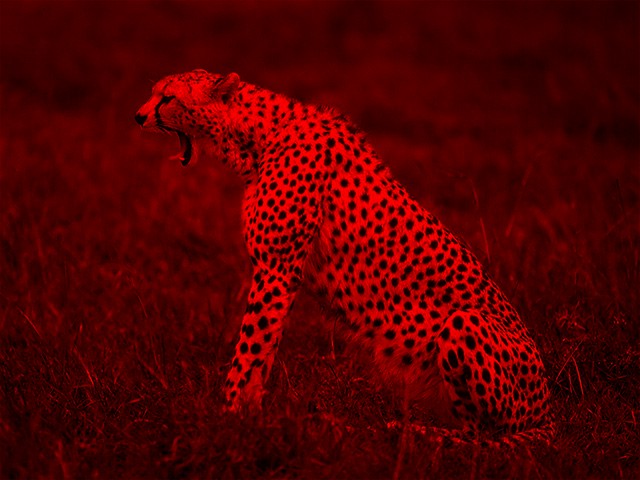

fun main() = application {
program {
val image = loadImage("data/images/cheeta.jpg")
extend {
drawer.drawStyle.colorMatrix = tint(ColorRGBa.RED)
drawer.image(image, 0.0, 0.0)
}
}
}
Inverting
Drawing an image with inverted colors can be achieved by using the invert color matrix.
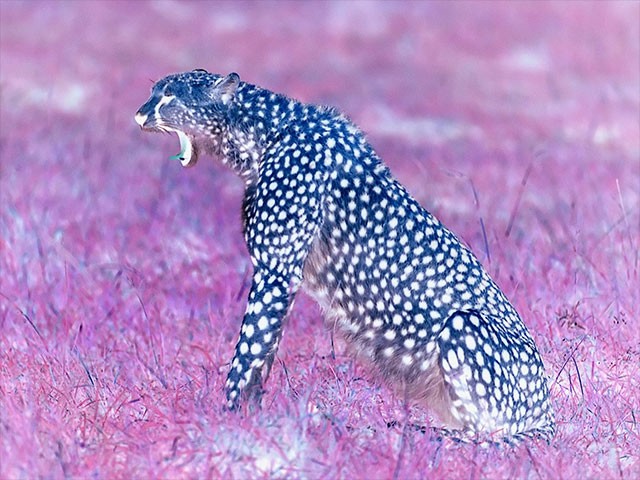

fun main() = application {
program {
val image = loadImage("data/images/cheeta.jpg")
extend {
drawer.drawStyle.colorMatrix = invert
drawer.image(image, 0.0, 0.0)
}
}
}
Grayscale
Drawing an image in grayscale can be achieved by using the grayscale color matrix.
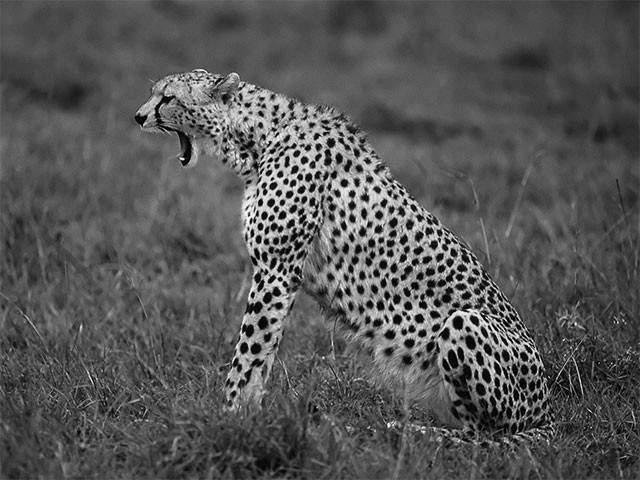

fun main() = application {
program {
val image = loadImage("data/images/cheeta.jpg")
extend {
// -- the factors below determine the RGB mixing factors
drawer.drawStyle.colorMatrix = grayscale(1.0 / 3.0, 1.0 / 3.0, 1.0 / 3.0)
drawer.image(image)
}
}
}
Concatenating color transforms
Color transforms can be combined using the multiplication operator. This is called transform concatenation. Keep in mind that transform concatenations are read from right to left, and in the following example we first apply the grayscale transform and then the tint transform.
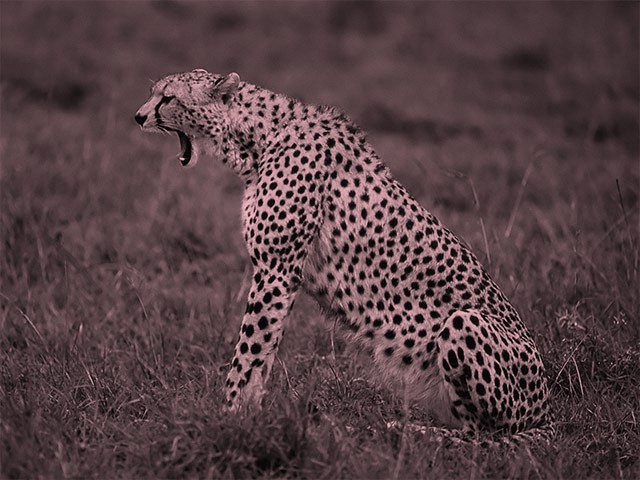

fun main() = application {
program {
val image = loadImage("data/images/cheeta.jpg")
extend {
// -- here we concatenate the transforms using the multiplication operator.
drawer.drawStyle.colorMatrix = tint(ColorRGBa.PINK) * grayscale()
drawer.image(image)
}
}
}